

IG3 assets and data contain sensitive information or functions that are subject to regulatory and compliance oversight. It builds upon the Safeguards identified in IG1 (56) and IG2 (74) totaling the 153 Safeguards in CIS Controls v8.Īn IG3 enterprise commonly employs security experts that specialize in the different facets of cybersecurity (e.g., risk management, penetration testing, application security). A major concern is loss of public confidence if a breach occurs. IG2 enterprises often store and process sensitive client or enterprise information and can withstand short interruptions of service.

Small enterprise units may have regulatory compliance burdens. These enterprises typically support multiple departments with differing risk profiles based on job function and mission.
20 CRITICAL SECURITY CONTROLS PDF INSTALL
Some Safeguards will depend on enterprise-grade technology and specialized expertise to properly install and configure.Īn IG2 enterprise employs individuals who are responsible for managing and protecting IT infrastructure. The 74 Safeguards selected for IG2 can help security teams cope with increased operational complexity. IG2 comprises 74 additional Safeguards and builds upon the 56 Safeguards identified in IG1. The Safeguards included in IG1 are what every enterprise should apply to defend against the most common attacks. IG1 is the on-ramp to the CIS Controls and consists of a foundational set of 56 cyber defense Safeguards. Implementation Groups (IGs) are the recommended guidance to prioritize implementation of the CIS Controls.ĬIS Controls v8 defines Implementation Group 1 (IG1) as basic cyber hygiene and represents an emerging minimum standard of information security for all enterprises. Using consensus process to collect best ideas.Maximizing the use of automation to enforce security controls, thereby negating human errors.Ensuring that security investments are focused to counter highest threats.Leveraging cyber offense to inform cyber defense, focusing on high payoff areas.Goals of the Consensus Audit Guidelines include The security controls give no-nonsense, actionable recommendations for cyber security, written in language that’s easily understood by IT personnel. The controls are designed so that primarily automated means can be used to implement, enforce and monitor them.
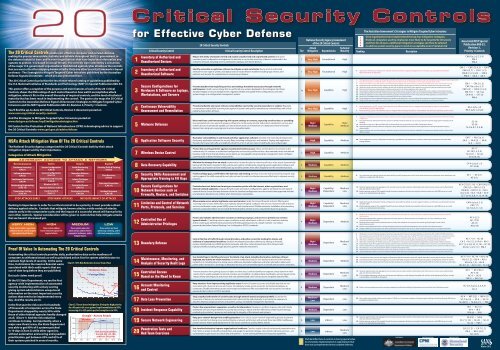
The guidelines consist of 18 (originally 20) key actions, called critical security controls (CSC), that organizations should implement to block or mitigate known attacks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
